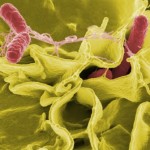
Lettuce Be Educated On E. Coli
E. coli is a type of bacteria that lives in the intestines of humans and animals. Usually, it is harmless. But, there are some strains that can make you very sick, causing stomach pains, nausea, and vomiting. E. coli has been in the news recently because of the outbreaks associated with romaine lettuce. Between March and April 2018, a total of 121 people in 25 states became ill with the bacteria according to the US Centers for Disease Control. There was one fatality associated with the outbreak. Ira Riklis has learned that the severity of the symptoms will depend on a person’s age and their current health.
Why Lettuce Is A Culprit
Leafy greens, such as lettuce, often become contaminated in the field. Such contamination can come from:
- Soil
- Water
- Animals
- Improperly composted manure
- Improper handling while harvesting, storing and transporting
In most cases, food contaminated with the E. coli bacteria is cooked which kills the bacteria. However, with fresh produce, such as romaine lettuce, people like to eat it fresh in salads. Although they may wash the lettuce, this may not be enough to get rid of the harmful bacteria. It only takes a small amount of the bacteria to make you sick. That means that if you take one bite of an undercooked burger or get a mouthful of contaminated pool water, you could get sick. Another reason why E. coli outbreaks are commonly associated with lettuce is that lettuce is the most popular produce item that is consumed. Other sources that are commonly associated with E. coli infections include:
- Ground Beef
- Unpasteurized Milk
- Contaminated Water
Symptoms
If you’ve been infected with one of the more serious strains of the E. coli bacteria, you’ll typically begin to notice symptoms three to four days after infection. However, in some instances, you will get symptoms within one day of infection or as long as a week after infection. The most common symptoms associated with an E. coli infection are:
- Diarrhea which can be mild and watery or severe and bloody
- Abdominal pain, cramping or tenderness
- Nausea and vomiting (although not everyone will experience this symptom)
If you notice that your diarrhea is severe and persistent, you should see your doctor as soon as possible because you will probably experience dehydration. Your doctor will be able to effectively treat your dehydration so that you will start feeling better. Small children, elderly people and those with a compromised immune system will suffer more severe symptoms as a result of an E. coli infection. It is absolutely necessary for such individuals to seek medical treatment. Most people will recover without treatment within one week after infection. It is important to drink plenty of fluids and get an adequate amount of rest.
E. Coli Prevention
Although you can’t always know when food is contaminated with E. coli, you can take some precautions to lessen the chance that you’ll get sick. Follow these tips to protect yourself from E. coli:
- Wash your hands before preparing any food, after diapering infants, after coming into contact with animals, their food or living environment.
- Use a food thermometer when cooking ground beef to ensure it has reached an internal temperature of 160 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Avoid eating high-risk foods such as undercooked beef, unpasteurized dairy products or juice, and alfalfa sprouts.
- Thoroughly wash all produce, especially lettuce.
The thought of contracting E. coli is scary. The illness it causes is certainly unpleasant and can be serious. But, that shouldn’t stop you from consuming your favorite foods, including romaine lettuce. The key is to safely handle your food. By taking the necessary precautions, you can lessen the chances that you or your family will be struck with the E. coli bacteria.