The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Gut Health
In recent years, gut health has moved from being a niche topic discussed among scientists and health enthusiasts to a mainstream concern. You’ve likely heard phrases like “trust your gut” or “gut feeling,” but in a biological sense, your gut does much more than guide intuition. It plays a crucial role in your overall health and well-being, influencing everything from digestion and immunity to mental health. In this guide, we’ll delve into the importance of gut health, the factors that influence it, and practical steps you can take to maintain a healthy gut.
What Is Gut Health?
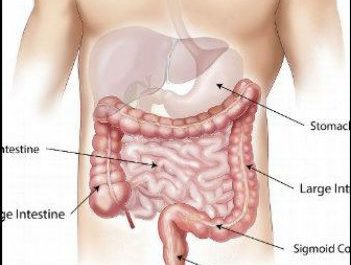
Gut health refers to the balance of microorganisms that live in your digestive tract. These microorganisms, often called gut flora or gut microbiota, include a wide variety of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes. While some of these are harmful, many are beneficial and play essential roles in maintaining your health.
A healthy gut is characterized by a balanced microbiome, which aids in digesting food, absorbing nutrients, and regulating the immune system. It also protects against harmful bacteria and toxins. When this balance is disrupted, it can lead to digestive issues, chronic inflammation, and even contribute to diseases like obesity, diabetes, and mental health disorders.
Why Gut Health Matters
The significance of gut health extends beyond just digestion. Here are some of the key reasons why maintaining a healthy gut is vital:
1. Digestive Health
The most apparent role of the gut is in digestion. A healthy gut efficiently breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates waste. When your gut is out of balance, it can lead to conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), constipation, diarrhea, and bloating.
2. Immune System Support
Approximately 70% of your immune system resides in your gut. The gut microbiome interacts with the immune cells, helping to regulate immune responses and prevent inflammation. A healthy gut barrier also prevents harmful pathogens from entering the bloodstream.
3. Mental Health Connection
The gut-brain axis is a communication network that links your gut and brain. This connection explains why gut health can influence your mood and mental well-being. An imbalanced gut microbiome has been linked to anxiety, depression, and even neurodegenerative diseases. The production of neurotransmitters like serotonin, which is primarily produced in the gut, is also dependent on a healthy gut.
4. Weight Management
Research suggests that gut bacteria play a role in regulating metabolism and weight. Certain bacteria can influence how the body stores fat, balances blood sugar, and manages energy. An unhealthy gut can contribute to obesity and metabolic disorders.
Factors That Affect Gut Health
Gut health is influenced by a variety of factors, some of which are within your control. Understanding these can help you make informed decisions to support a healthy gut.
1. Diet
What you eat has a significant impact on the composition of your gut microbiome. Diets high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can harm gut bacteria, leading to an imbalance. On the other hand, diets rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods promote a healthy gut.
2. Antibiotics
While antibiotics are essential for treating bacterial infections, they can also disrupt the gut microbiome by killing both harmful and beneficial bacteria. It’s crucial to use antibiotics only when necessary and to restore gut health afterward through probiotics and a healthy diet.
3. Stress
Chronic stress can negatively affect gut health. Stress hormones can alter gut motility and increase inflammation, leading to an imbalanced microbiome. Practicing stress management techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and exercise can help maintain gut health.
4. Sleep
Poor sleep quality and irregular sleep patterns can disrupt the gut microbiome. Ensuring adequate, quality sleep supports overall health, including the health of your gut.
5. Physical Activity
Regular exercise promotes gut health by enhancing the diversity of the gut microbiome. Physical activity helps with digestion, reduces stress, and supports overall well-being, all of which contribute to a healthy gut.
How to Improve and Maintain Gut Health
Taking care of your gut is crucial for maintaining overall health. Here are some practical steps you can take to improve and sustain a healthy gut.
1. Eat a Diverse, Fiber-Rich Diet
A varied diet rich in fiber from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes nourishes beneficial gut bacteria. These bacteria ferment fiber into short-chain fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory effects and support gut health.
2. Include Fermented Foods
Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha contain probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that can enhance the diversity and balance of your gut microbiome.
3. Take Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics are supplements that contain live beneficial bacteria. Prebiotics are types of fiber that feed the good bacteria in your gut. Both can be helpful in maintaining a healthy gut, especially after taking antibiotics or during times of stress.
4. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential for digestion and maintaining the mucosal lining of the intestines. It also helps in balancing the good bacteria in the gut.
5. Manage Stress
Incorporate stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity into your daily routine. Reducing stress can positively impact your gut health.
6. Get Enough Sleep
Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Establish a regular sleep routine, and create a relaxing sleep environment to support your overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding and maintaining gut health is crucial for your overall well-being. By adopting a balanced diet, managing stress, staying active, and getting enough sleep, you can support a healthy gut. Remember, the journey to better gut health is a gradual process, but with consistent effort, the benefits for your digestion, immunity, mental health, and more will be well worth it.
Your gut is more than just a part of your digestive system—it’s a cornerstone of your health. Take care of it, and it will take care of you.